Cloud storage security: top providers' security compared
Microsoft OneDrive is a consistent performer across all categories

The benefits of cloud storage in an enterprise context are many, and most businesses today rely on it for some or all of their day-to-day operations. However, the shift from on-premises (on-prem) storage to the cloud presents new security risks alongside the benefits.
Cloud storage, when misused, can lead to catastrophic data loss incidents, IP theft, or malware infection. The potential cost to businesses is huge, and that’s before we even consider the litigation that can emerge from these types of incidents.
Fortunately, the best cloud storage providers are highly secure and can almost guarantee that your business won’t endure time-consuming and costly setbacks. This article compares cloud storage security across several categories, helping you determine which providers are the best cloud storage fit for your organization.
How to choose the most secure platform
Why you can trust Tom's Guide
Today, the cloud storage market is very competitive, and most of the top providers offer a similar set of security features. Determining which platforms are the most secure requires an in-depth comparison across four categories: encryption, account security, redundancy and geo-replication, and administrator controls - which is exactly what we will do here.
Encryption

Top-quality encryption is non-negotiable when it comes to secure cloud storage, because it makes your data indecipherable to unauthorized persons.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) 256-bit encryption is an industry standard that can be used to protect data at rest (when stored on your provider’s servers), while SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) encryption (at either 128 or 256-bit AES standard) is commonly used to encrypt data in transit (when data is moving between servers).
As a general rule of thumb, 256-bit AES encryption is more secure than 128-bit. End-to-end encryption is the top level of encryption, ensuring only account users can access data. This is achieved by providing the user with a set of encryption keys that are stored locally on the user’s device.
To decrypt the data, the personalized encryption keys must be used, tying data access to trusted devices. Using end-to-end encryption means that not even your provider can access your files.
We think the best providers are those that include unlimited end-to-end encryption, such as pCloud and IDrive. pCloud includes end-to-end encryption with all business plans, while IDrive enables administrators to manage their own encryption keys (thereby enabling end-to-end encryption). Read our pCloud review, our IDrive personal cloud backup review and our IDrive business review to learn more.
Microsoft OneDrive also includes a feature called Vault, which is a sub-folder with end-to-end encryption. Unfortunately, though, files have to be added one by one, making it a poor choice for use at an organization-wide level. Read our OneDrive review and our OneDrive for Business review to find out more about the service.
Providers such as Dropbox (256-bit at rest and 128-bit in transit), Google Drive (128-bit at rest and 256-bit in transit), and Apple iCloud (128-bit both in transit and at rest) provide advanced levels of encryption, but without end-to-end encryption. You can learn more about all three providers in our Dropbox review, our Dropbox for Business review, our Google Drive review, and our iCloud review.
Account security
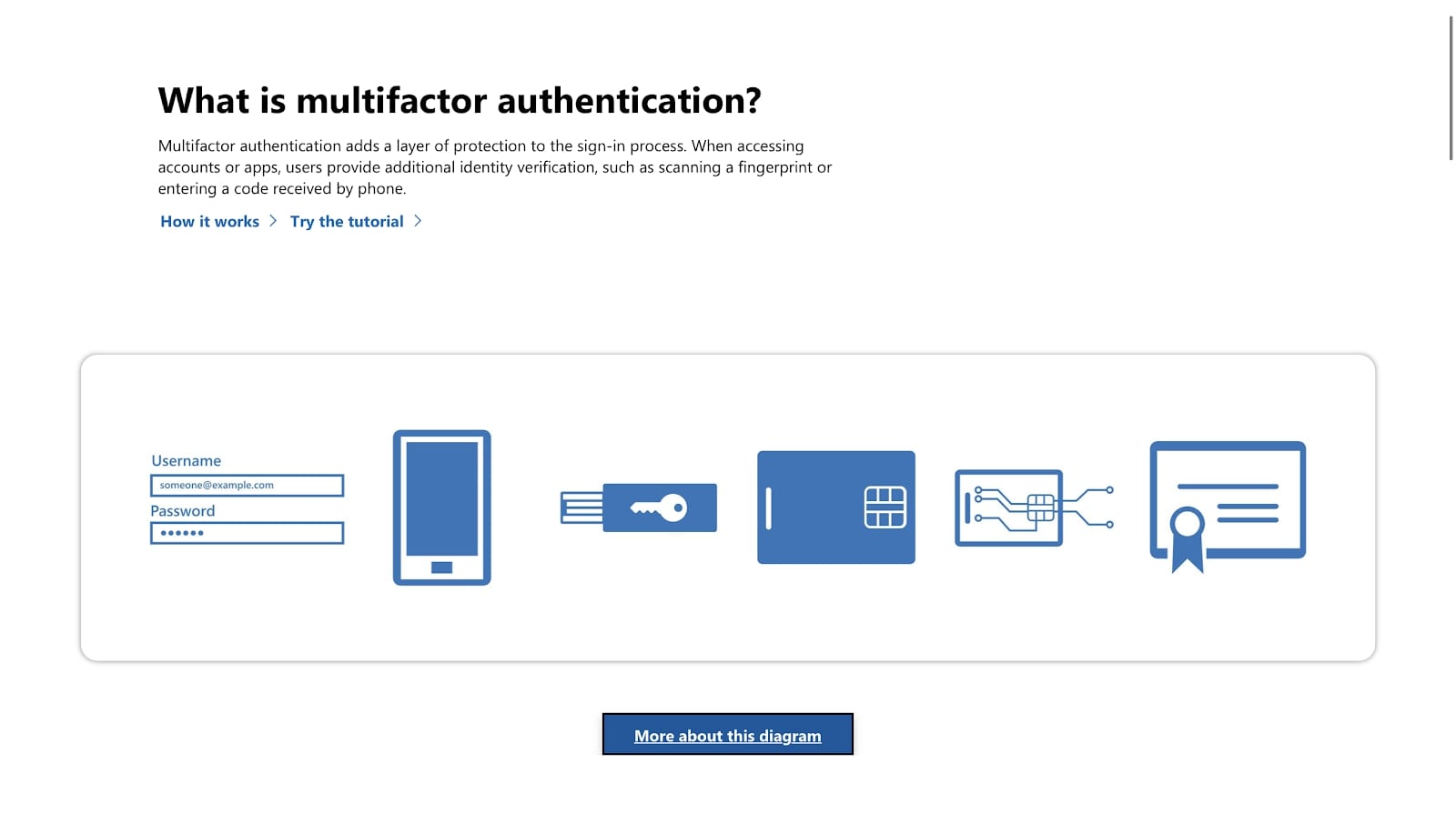
No amount of encryption can protect your data if you or your employees’ accounts are compromised. Once a cybercriminal has accessed an employee’s account, they can access and edit all stored files that the employee has access to.
Account security, therefore, is absolutely essential if you want to use cloud storage safely and securely. The most critical account security features are password standards enforcement, dictating how strong a password must be; and two-factor authentication (2FA), which adds a second pillar of security to a user's account.
Password standards enforcement enables administrators to require that all employee passwords meet specific criteria. Most commonly, these criteria will be a minimum password length and a requirement to include special characters. Insecure passwords are one of the top reasons that accounts are hacked, so requiring employees to create strong ones is a simple yet effective solution.
2FA is another security policy that is crucial for protecting employee accounts. It requires employees to provide both a password and a secondary means of authentication when logging into their account. The second method is typically a code generated in an authenticator app or sent to the user’s mobile or email address. 2FA makes it extremely unlikely that your employee’s account will be compromised.
Each of the seven platforms considered in this article provides both password standards enforcement and 2FA. However, we think Microsoft OneDrive and Google Drive earn extra points due to a more comprehensive 2FA framework across their range of software platforms.
Redundancy and geo-replication
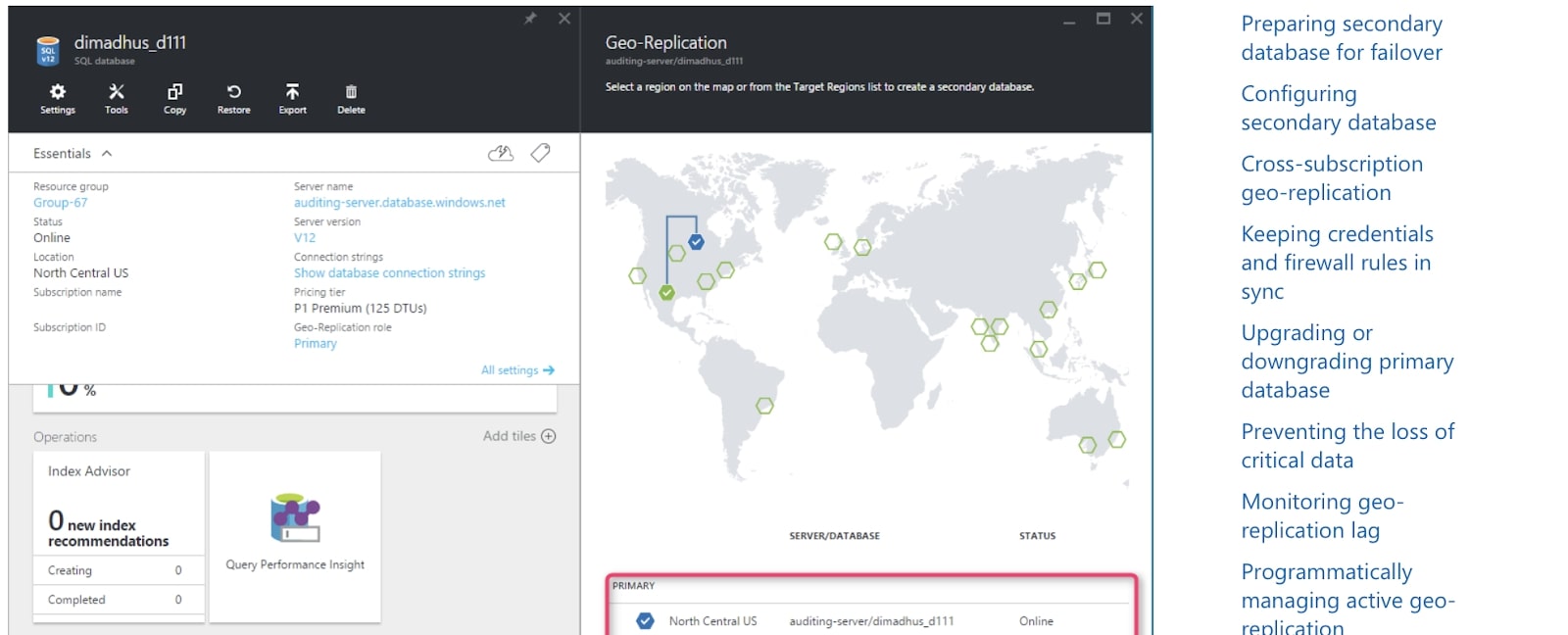
Organizations relying on cloud storage need to know their data will always be available, even if there is a major disruption of service at a particular data center or across an entire region.
The best cloud storage platforms have redundancy policies across their networks, including geo-replication of data across several data centers and regions. This means that copies of your organization’s data are stored across several locations, reducing the likelihood your data will be unavailable.
The market leader in this area is undoubtedly Microsoft, with over 160 data centers in a truly impressive global network. Google is quite far behind with only 21 data centers. However, each of these data centres is a massive operation with hundreds of on-prem employees. In addition, both companies manage enterprise cloud storage solutions (Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud) for large transnational corporations.
The other providers included in this article all provide some level of geo-replication and data redundancy, but the precise level of service is often unclear. It’s also important to mention that these providers usually don’t own and maintain their own data centers, but contract out to third-parties. This doesn’t necessarily make them less secure, but means there are more potential points of vulnerability.
Administrator controls

The final piece of the secure cloud storage puzzle is a robust suite of administrator controls. This is because encryption, secure accounts, and robust data redundancy policies amount to nothing if your employees misuse the platform, whether negligently or maliciously.
Therefore, all business owners should look for account auditing and role-based permissions in a secure cloud storage solution. Account auditing enables administrators to generate usage reports quickly, and identify potential security risks before they become major issues. Audits also enable administrators to see which files are being accessed and by whom.
Role-based permissions enable business leaders to control the types of files each employee has access to, allowing you to ensure sensitive or private files are only accessible to those who need access.
Most of our providers offer an impressive suite of administrator controls, but we think Dropbox stands out due to its dedicated admin console for all business customers. It goes above and beyond what is offered by the other platforms.
At the other end of the spectrum, unfortunately, is Apple iCloud. Apple doesn't really target its software to business owners, so it often lacks when it comes to administrator controls.
Conclusion
In sum, to choose a secure cloud storage platform for your business, you need to consider encryption, account security, redundancy and geo-replication, and administrator controls. The table below compares the platforms discussed in this article and their capabilities in relation to each of the points we've covered.
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Encryption | Account security | Redundancy and geo-replication | Administrator controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft OneDrive | A | A | A+ | A |
| IDrive | A | B+ | B | B+ |
| Google Drive | B- | A | A+ | B+ |
| Apple iCloud | A- | B+ | B | C |
| Dropbox | B | B+ | B | A+ |
| pCloud | A+ | A+ | B | B |
It is only when you compare providers across these categories that the best platform for your individual needs will become apparent. Taking the time to find a platform that will integrate seamlessly into your organization is a decision that will pay dividends for many years to come.
Learn more about cloud storage security in a range of our features focusing on the subject, including: why cloud storage is secure, featuring tips on how to use it securely; and what you should look for in secure cloud systems.
Get instant access to breaking news, the hottest reviews, great deals and helpful tips.

Darcy is a freelance copywriter, and a candidate for the dual master's program between the Paris Institute of Political Studies (Sciences Po) in France and Peking University in Beijing, China. His academic and professional areas of interest include human rights and development, sustainable agriculture and agroecology, Pacific Islands diplomacy, and Sino-Australian relations.
 Club Benefits
Club Benefits





