PHOLED looks like the future of TVs — here’s why
UDC opens new factory to ramp up PHOLED production for OLED displays

Here at Tom’s Guide our expert editors are committed to bringing you the best news, reviews and guides to help you stay informed and ahead of the curve!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Daily (Mon-Sun)
Tom's Guide Daily
Sign up to get the latest updates on all of your favorite content! From cutting-edge tech news and the hottest streaming buzz to unbeatable deals on the best products and in-depth reviews, we’ve got you covered.

Weekly on Thursday
Tom's AI Guide
Be AI savvy with your weekly newsletter summing up all the biggest AI news you need to know. Plus, analysis from our AI editor and tips on how to use the latest AI tools!

Weekly on Friday
Tom's iGuide
Unlock the vast world of Apple news straight to your inbox. With coverage on everything from exciting product launches to essential software updates, this is your go-to source for the latest updates on all the best Apple content.

Weekly on Monday
Tom's Streaming Guide
Our weekly newsletter is expertly crafted to immerse you in the world of streaming. Stay updated on the latest releases and our top recommendations across your favorite streaming platforms.
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
If you’ve never heard of PHOLED, you’re not alone. The technology is already partially at the core of the best OLED TVs and soon TVs from Samsung and LG could be using it entirely for the subpixels in every OLED display pixel.
The company behind PHOLED is betting on PHOLED being the future. Universal Display Corporation (UDC) has been making PHOLED — which stands for phosphorescent organic light emitting diode — for years and now is expanding its operations. The company just announced the opening of a new PHOLED manufacturing plant in Shannon, Ireland to manufacture more of its signature phosphorescent materials for OLED displays.
Our phosphorescent OLED (PHOLED) materials and technology can be found in virtually every commercial OLED product around the world
Janice Mahon, UDC
While the factory was just officially unveiled to the world, UDC and its partner PPG have been working on this new E.U. factory for a while now. According to Janice K. Mahon SVP, Technology Commercialization & GM, Commercial Sales Business at Universal Display Corporation, the factory has been in development since February 2021 and has already begun production.
UDC could not specify which customers will be serviced by this new plant — LG Display and Samsung Display have recently been tipped to adopt fully PHOLED TV displays in the near future — but Mahon did state that the factory will “service existing and future customers whose display products require UDC’s state-of-the-art, energy-efficient phosphorescent OLED emissive materials” and that PHOLED materials have already started rolling out to display makers. Clearly, UDC expects that PHOLED isn’t going away anytime soon.
What is PHOLED and why does it matter?
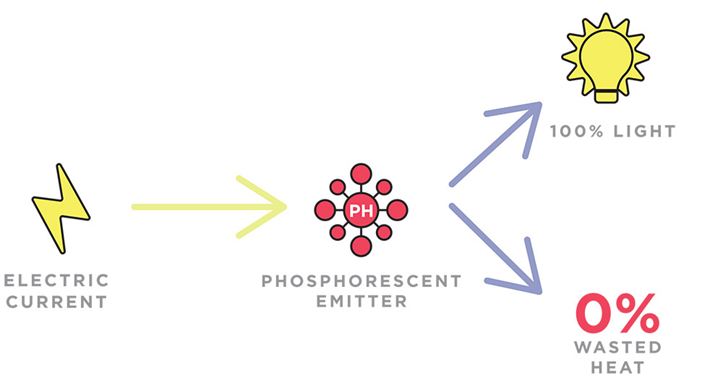
Currently, OLED displays already partially use PHOLED technology. An OLED pixel is made up of three subpixels: red, green and blue (RGB), though LG OLED TVs add a fourth white subpixel. These subpixels are either phosphorescent subpixels or fluorescent subpixels — and these aren’t created equal.
The biggest difference? Fluorescent subpixels are significantly less power efficient. In fact, Mahon says fluorescent subpixels are just 25% as efficient as their phosphorescent counterparts.
Most OLED displays already use red and green phosphorescent subpixels developed by UDC. In fact, Mahon says that UDC PHOLED materials are "found in virtually every commercial OLED product around the world." But everyone still uses fluorescent blue subpixels — largely because UDC is still developing a phosphorescent alternative (Mahon says blue PHOLED is still in R&D).
Get instant access to breaking news, the hottest reviews, great deals and helpful tips.
However, with this new factory in Ireland, UDC could quickly ramp up production of blue PHOLED subpixels to quickly transition the OLED TV market to fully PHOLED displays. And that’s good news because significantly more efficient TVs would be a major upgrade for everyone.
More from Tom's Guide
- LG and Samsung reach historic OLED TV deal — what it means for you
- GTA 6 release date looks set for 2024 — here’s the proof
- Memorial Day TV sales 2023 — best early sales now

Malcolm has been with Tom's Guide since 2022, and has been covering the latest in streaming shows and movies since 2023. He's not one to shy away from a hot take, including that "John Wick" is one of the four greatest films ever made.
 Club Benefits
Club Benefits










