AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud vs IBM Cloud: What’s the best cloud environment?
We look at unique features, performance, and pricing to help clarify this complex decision

Here at Tom’s Guide our expert editors are committed to bringing you the best news, reviews and guides to help you stay informed and ahead of the curve!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Cloud computing refers to the on-demand delivery of computer resources like storage space, processing power, and bandwidth, and is quickly becoming the preferred workspace for businesses both large and small.
Services in the cloud space include the best cloud storage providers as well as other cloud platforms - switching between cloud environments is no easy task, however, which makes your initial choice of provider all the more important.
Here, we’ll take a look at four of the most popular cloud platforms on the market: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud. By comparing features, customer support, and pricing, we hope to facilitate your decision in figuring out which is best for your business.
Article continues belowAmazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS has an extensive features list, some absent from competitors. The AWS Scheduler saves time and money, and an OS for microcontrollers is ideal for businesses developing “smart” devices. Built-in online billing meters usage based on prices you set, while it also includes API support for third-party software. AWS is a decidedly safe choice, and pricing is often the lowest.
Microsoft Azure
Azure also has many features available, and excels in disaster recovery and scheduling via the Azure Logic App, simplifying the jobs process with scheduled or rules-based execution. Support costs $100 a month which, alongside good response times, means it offers the best level of basic support at the most reasonable price.
Google Cloud
Google offers “Preemptible VMs,” short-lived virtual machines capable of running batch processes. Having also spent years creating extensive global networks, its competitive support pricing and global standing put it in good stead.
Features
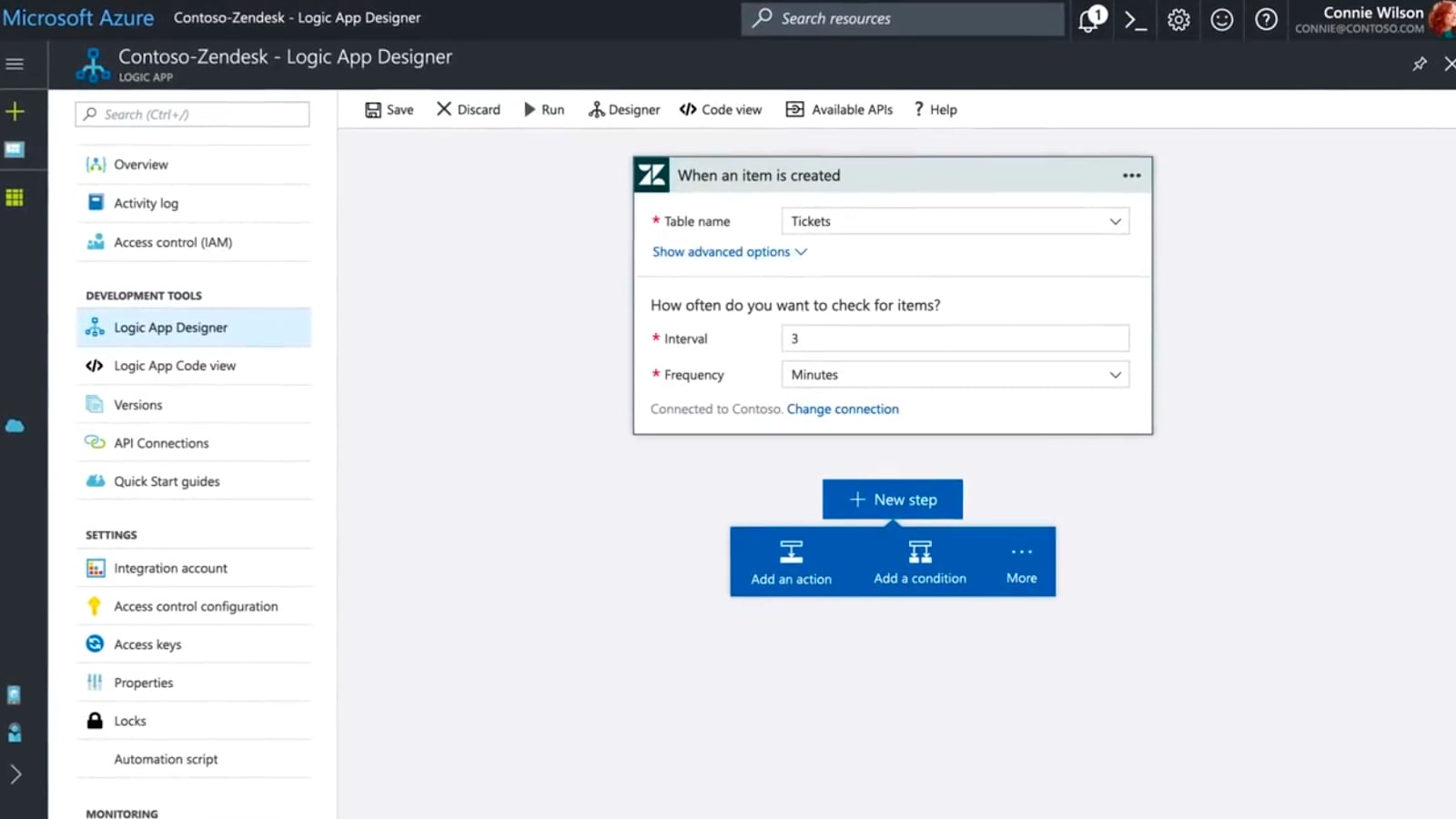
AWS and Azure hold respectively 30% and 20% of the market share, and for good reason: they both come with an extensive features list. While most key features are shared by all four providers, some specific ones are absent from one or more platforms, which can help you make your decision.
If you’re interested in a hybrid storage solution, you may want to take IBM and Google off your list, as neither supports hybrid storage natively. It is possible to integrate a third-party application to get the job done, but in our experience, this leaves more room for error.
Similarly, Google Cloud doesn’t offer a simple solution for cloud-based backup of virtual environments - and both Google and IBM fall short in disaster recovery, where AWS and Azure excel.
If job orchestration is another important feature for you, then IBM probably won’t meet your needs, as its batch-processing capabilities are limited compared to AWS Batch and Azure Batch. Google offers “Preemptible VMs,” which is a suitable solution: short-lived virtual machines capable of running batch processes.
Get instant access to breaking news, the hottest reviews, great deals and helpful tips.
One area where Azure and IBM actually pull ahead of AWS (and Google) is in scheduling. IBM’s Workload Scheduler and Microsoft’s Azure Logic App make it easy to run individual jobs, with scheduled or rules-based execution. AWS Scheduler has a similar functionality, but enables the starting and stopping of whole EC2 and RDS instances: a time- and money-saving feature, but one that lacks the granular control of Azure and IBM’s solutions.
While all four providers offer IoT functionality, data analytics, trigger functions, and specific IoT security, only Amazon offers an operating system for microcontrollers - like those used in machinery and appliances - which makes it easy to connect such devices to the cloud and benefit from the platform's services. Businesses interested in developing flexible, highly extensible “smart” devices will want to give heavy preference to AWS.
Many third-party solutions exist for monetizing a service built on your cloud platform, but it’s worth mentioning that AWS has built-in online billing capabilities: sign up customers and meter their usage of services, and Amazon will bill them based on prices you’ve set.
Performance
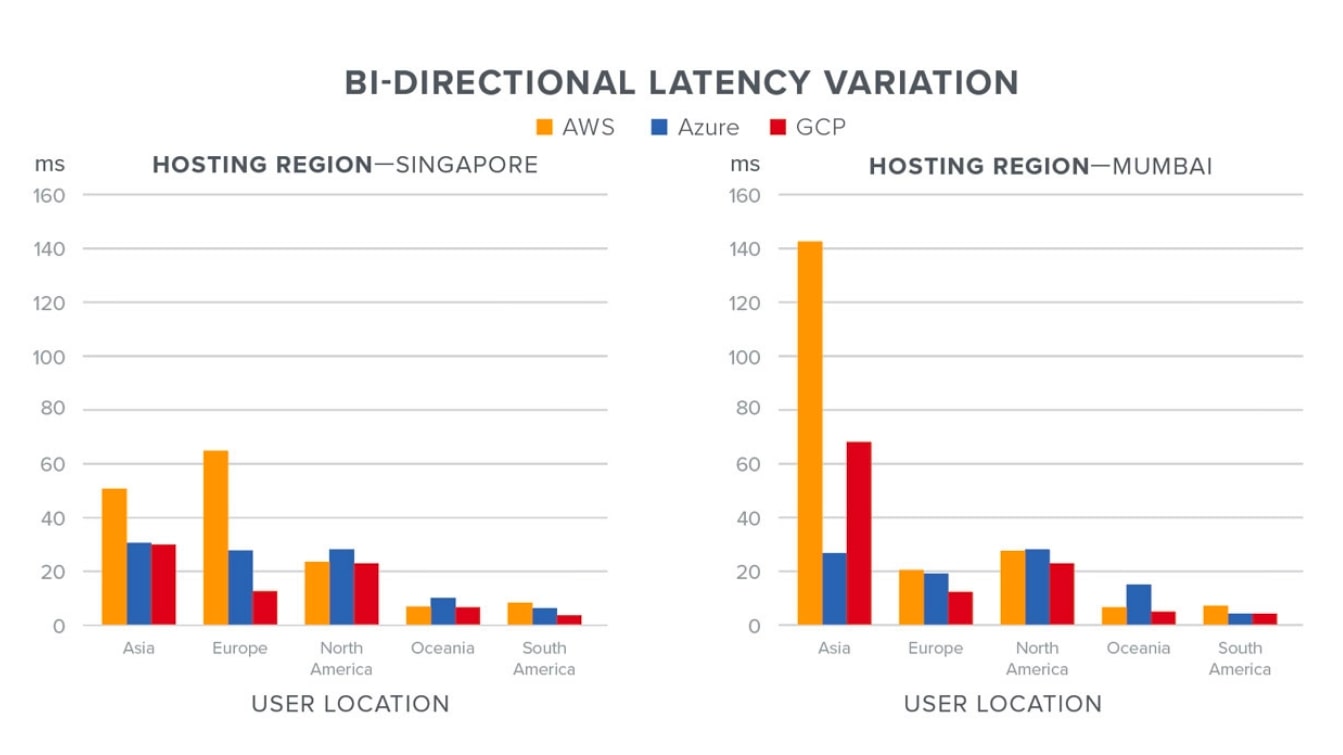
According to a study by network intelligence specialist ThousandEyes, there are some important differences in performance between these top providers. First, Microsoft and Google have spent decades building out extensive, global, private networks, whereas AWS relies heavily on the public internet.
While the platform is investing in infrastructure, it nonetheless demonstrates the highest latency levels in several regions, including Asia and Europe. That said, geography is a key factor in determining performance, and no cloud provider has managed global consistency.
You’ll want to look at where most of your data is coming from, and where it has to travel based on your business’ activities, to accurately compare speed and stability.
Support
Support is another area where cloud providers differ greatly. Free technical support is pretty limited in each case, but especially so with Azure and Google. AWS has no free support plan. The least extensive of these is Google, whose free plan only covers billing issues, while AWS and Azure are business-hours only by email. Conversely, IBM offers 24/7 support through a ticket system with its free plan.
The next tiers up, which will interest most SMBs, vary in pricing. AWS starts at $100, but rises sharply as a percentage of overall AWS costs (if you spend $10,000 a month on AWS, support costs an additional $1,000). Google costs $100 a month per user, while IBM starts at $200 and goes up “based on consumption”. Azure costs $100 a month, which makes it stand out in this category.
It also has good response times (especially compared to AWS, whose listed response time at this tier falls behind all three other services), although it doesn’t include API support or third-party software, which AWS does.
Support plans are complex, and warrant much closer examination based on what issues your business is likely to encounter. That said, the best level of basic support at the most reasonable price seems to be offered by Azure.
Pricing and plans
Like support plans, general pricing plans are extremely complex. Your very best bet is to schedule sales calls with any providers you haven’t eliminated based on features and support, and get a quote.
Pricing is generally provided on a per-service basis, so it’s difficult to provide even very general comparisons, as use cases vary widely. Similarly, each provider offers a wide array of discount pricing based on service commitments, resource use, operating system, and more.
According to RightScale Cloud Management, however, AWS outperforms Azure, Google, and IBM in a majority of use-cases.
Verdict
Comparing cloud-computing platforms is no easy task, and if you still don’t feel like you’ve been able to settle on one after this article, that’s perfectly normal. We’ve tried to give an overview of some of the most important use-case differences that may help small businesses, if not make a confirmed choice, at least eliminate one or two platforms from the running.
So much of making this decision depends on your business’s goals, resources, and workflows. While we can’t designate a single winner, AWS is a decidedly safe choice for most businesses. It has a huge number of features, some of which are completely absent from its competitors, and while it lags behind in some performance indicators, its pricing in many cases ends up being the lowest.
To learn more about a number of the systems compared here, read our AWS review, our Microsoft Azure review, and our Google Cloud review.
Christian is a freelance writer and content project manager with over six years' experience writing and leading teams in finance and technology for some of the world's largest online publishers, including TechRadar and Tom's Guide.
 Club Benefits
Club Benefits















