12 computer security mistakes you're probably making — and what to do instead
If you're doing any of these things, it's time to stop

If you've ever owned a car in a city, you may know the rule about break-in's: It's not that you'll never get broken into, but more about making your vehicle look the least attractive to thieves by making sure you don't leave valuables in plain sight while keeping your doors locked and parking in well lit places.
When it comes to computer security practices, many of the same philosophies apply – you're basically looking to maintain the best practices at all times to make sure that your system is the least attractive to hackers spreading malware, infostealers and ransomware. How do you do that? Well, funny you should ask...
1. Avoid, ignoring or postponing updates

Among the common reasons that people don’t update their software are: an unwillingness to interrupt their work or tasks, a fear of bugs or flaws in the new update and a reluctance to change a familiar interface.
These are all understandable enough, however when you don’t update your operating system, software or antivirus suite what you’re essentially doing is leaving giant holes open making it particularly easy for hackers to access your system.
Many software updates can be automated or scheduled around a convenient time so it’s best to make sure you don’t avoid updates or leave your machine vulnerable when possible
2. Hanging on to older versions of applications
Even after you’ve updated a program, don’t forget that some older versions may not automatically update or remove themselves after a new version is installed.
Just like with un-updated software, keeping an old version of a program on your system alongside a new one is essentially a gateway that a hacker can exploit. It’s like a giant hole in a fence that any thief could walk through which basically renders the fence meaningless.
Get instant access to breaking news, the hottest reviews, great deals and helpful tips.
3. Disabling User Account Control (UAC) features
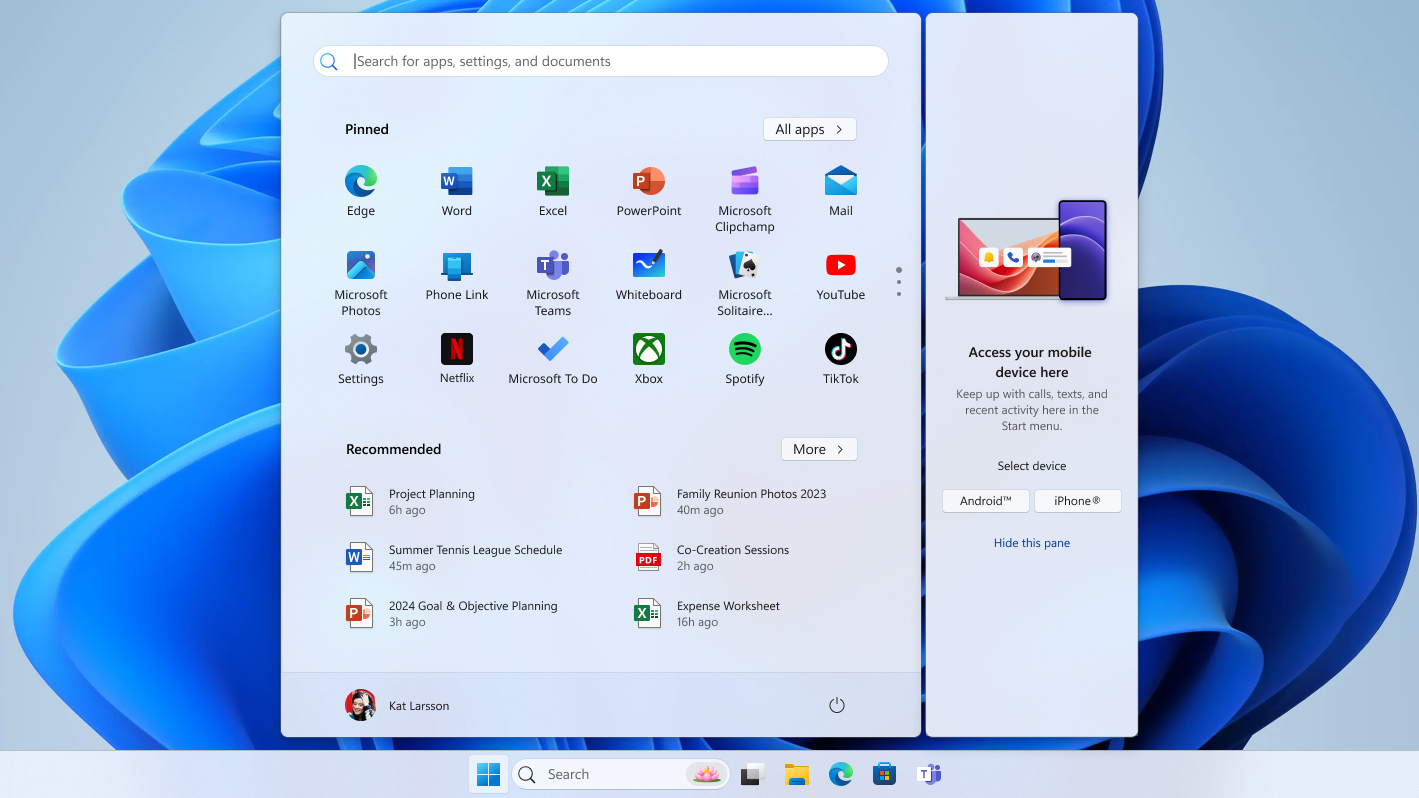
The “User Account Control” feature sends an alert whenever a program tries to make changes to Windows settings and particularly anything that would require Admin privileges.
If it’s disabled, that means you get absolutely zero warning if a program (either benign or malicious) attempts to make any changes to the Windows operating system. The only benefit is you get slightly fewer pings and alerts, and the downside is… far greater than that, so it's best to leave this one enabled even if it is a little annoying.
4. Clicking on any link, QR code, attachment or file

There is no quicker way to infect your computer with malware than to click on all the things.
In fact, don't just click on anything you receive via email or in a message is one of the pieces of advice we include in almost every article we write about malware for a reason. You really, really shouldn’t do it.
That link in an unexpected text message? Don’t click it. A random attachment sent by a stranger in an email? Don’t click it. A download button on a website that just popped up while you were browsing? Yep. You guessed right – don’t click it.
Unless it’s something you were expecting, and you know the sender, do not under any circumstances click that link, extension, file, download, code or attachment.
5. Downloading programs from anywhere

One of the fastest ways to pick up malware, ransomware, infostealers or other malicious software is to put them on your computer yourself via a quick Google search and clicking on the first downloadable result for whatever service or software you’re on the hunt for.
An easy rule to follow is to make sure you’re always downloading apps and software from an official website or app store. It’s honestly not that much harder to make sure you’re at the correct site or app store to start with, so why risk winding up with a malicious file?
6. Piracy, cracks and keygens

Though it may seem easy enough to poke around on the web to find one of the many of dozens of cracked files or keygens for a slightly-less-than-legal copy of Windows or Adobe Photoshop in order to save some cash, it’s certainly going to cost you way, way more.
Especially when you realize that what you’ve actually downloaded is a malicious file that’s stolen a bunch of your personal data and credit card information.
Downloading pirated software or other content online is the easiest and quickest way to end up with a malware infection. So don't do so yourself and make sure that everyone in your household isn't either.
7. Shortlinks

Though not as popular as they once were, shortened URL services like bit.ly and TinyURL were once used much more frequently.
While they certainly have plenty of legitimate uses, they’re also perfect for concealing a link’s true destination. Which means if users don’t have any sort of link preview add-on in their browser, these little links can be an ideal vector to get victims to navigate blindly to phishing sites or to downloading malicious files.
8. Using open, unsecured Wi-Fi

It doesn’t really matter if you’re connecting to an open guest account at the local laundromat, or if you’ve just left your own network open to everyone.
Either way, it’s a genuinely bad idea. First, if you’re connecting to random open, unsecured Wi-Fi networks, please just start using cellular data instead. And if you’ve been leaving your own wireless network open and unsecured, now is the time to fix that as well.
Unsecured Wi-Fi routers are an incredibly common way for malware to enter your network, and it’s easy to get started securing your wireless router.
These days, many of the best Wi-Fi routers and the best mesh Wi-Fi systems ship with security software built-in. However, it's up to you to configure it and keep it updated.
9. Surfing on an administrator enabled account
Something that is actually a pretty easy security fix right out of the gate is to make sure you’re using a Standard account and not an Administrator account.
Though it may seem useful to be operating under an Admin account because it offers you more access and control, a lot of different types of malware and exploits actually won’t run if you’re using a Standard account. So, if you need to use your Administrator account, switch over and then switch back because you’re actually protecting your machine by doing so.
10. Using an outdated operating system
Look, it’s fine if your car is a classic, your decor is vintage and your music taste isn’t current – but your operating system absolutely should be.
Sure, Windows 10 is a perfectly fine OS but it was released in 2015 and that was a decade ago. Think about the amount of things that have changed, technologically, in the past decade.
Patches and updates can only do so much and the reality is that older operating systems, in addition to being rife with potential security vulnerabilities, can also leave you with a machine that has various performance problems or compatibility issues. No one needs their machine to run harder, just so it can have a higher risk of being infected by exploits and security leaks.
It's also worth noting that if you're still using Windows 10, you have until October 14 of this year to upgrade to Windows 11. After that time, Windows 10 will no longer receive new security updates and patches which puts people still using this version of Windows at serious risk of getting hacked.
11. Using the same password everywhere

You know better. You really do. But every time you need to start an account for a new fitness app you impulsively decided to download, purchase a piece of furniture from a new website, or caved into signing up for a new streaming service you’re going to need to register and create a strong, unique password.
Many of us are guilty of being lazy and reusing passwords, which is just a bad habit that leaves our accounts open to being easily hacked.
If you don’t have one of the best password managers yet, get one. That way you can go back to being lazy! Or better yet, set up a passkey on your mobile device. But at the very least make your password a phrase instead of any of the easy to guess options like 12345.
12. Not using antivirus software

Do you drive without a seatbelt? Probably not. You also probably have smoke alarms in your house, and lock your front door when you leave. You should also have one of the best antivirus software suites on your computer.
Unless for some reason, you’re intentionally interested in leaving your system available for viruses, there’s no reason not to install any of the many free or paid options out there.
Even the safest, hyper-vigilant online habits can only take you so far and all it takes is a one wrong click on a site that’s been hijacked, or falling for the most convincing phishing link in an email, and you’re toast.
More from Tom's Guide
- 5 common mistakes people make when shopping for antivirus software
- How does antivirus software work?
- Dangerous new Windows malware hides from your antivirus while impersonating a popular PC brand

Amber Bouman is the senior security editor at Tom's Guide where she writes about antivirus software, home security, identity theft and more. She has long had an interest in personal security, both online and off, and also has an appreciation for martial arts and edged weapons. With over two decades of experience working in tech journalism, Amber has written for a number of publications including PC World, Maximum PC, Tech Hive, and Engadget covering everything from smartphones to smart breast pumps.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
 Club Benefits
Club Benefits





