Battery Fueled By Air Could Power Cars, Laptops
According to researchers at the University of St Andrews, the St. Andrews Air battery (STAIR) may be the ticket to a new era of laptops, mobile devices, and electric cars, discarding traditional chemicals and using air as a source of power.
Here at Tom’s Guide our expert editors are committed to bringing you the best news, reviews and guides to help you stay informed and ahead of the curve!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Daily (Mon-Sun)
Tom's Guide Daily
Sign up to get the latest updates on all of your favorite content! From cutting-edge tech news and the hottest streaming buzz to unbeatable deals on the best products and in-depth reviews, we’ve got you covered.

Weekly on Thursday
Tom's AI Guide
Be AI savvy with your weekly newsletter summing up all the biggest AI news you need to know. Plus, analysis from our AI editor and tips on how to use the latest AI tools!

Weekly on Friday
Tom's iGuide
Unlock the vast world of Apple news straight to your inbox. With coverage on everything from exciting product launches to essential software updates, this is your go-to source for the latest updates on all the best Apple content.

Weekly on Monday
Tom's Streaming Guide
Our weekly newsletter is expertly crafted to immerse you in the world of streaming. Stay updated on the latest releases and our top recommendations across your favorite streaming platforms.
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
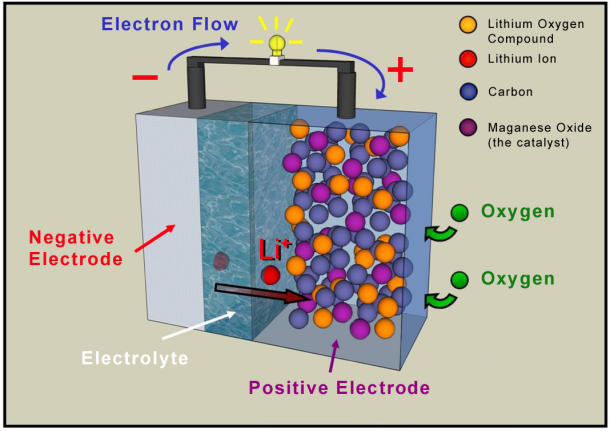
According to researchers at the University of St. Andrews, the St. Andrews Air battery (STAIR) may be the ticket to a new era of laptops, mobile devices, and electric cars, discarding traditional chemicals and using air as a source of power.
While the overall design has not been finalized, the researchers behind the project say that the air-fueled battery could present ten times the energy capacity of rechargeable lithium batteries currently available on the market.
“Our target is to get a five to ten fold increase in storage capacity, which is beyond the horizon of current lithium batteries. Our results so far are very encouraging and have far exceeded our expectations,” said Professor Peter Bruce of the Chemistry Department at the University of St Andrews.
Rather than using the traditional chemical constituent, lithium cobalt oxide, the STAIR battery utilizes porous carbon. Oxygen is freely drawn in from the air and reacts within the pores of the carbon component, creating a constant "flow" of energy, or as Bruce states, a reagent, continuously recharging the battery as it discharges. Because the battery doesn't require chemicals, it offers more energy for the same size battery currently available on the market, and is relatively cheaper than its chemical-based comrades.
Currently the research project reaches its halfway mark in July. Entitled "An O2 Electrode for a Rechargeable Lithium Battery," the research began on July 1, 2007, and is expected to end on June 30, 2011. The primary focus of the project is to understand how the chemical reaction of the battery works, and how to improve it. The team plans to create a STAIR cell prototype that can work in a cell phone or MP3 player, however the battery will more than likely not see a commercial release for at least another five years.
While the project is being led by Bruce and the research group over at the University of St Andrews, Strathclyde and Newcastle are also pitching in to provide additional help. The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) is providing the funding for the project, with £1,579,137--almost 2.2 million USD--donated thus far.
Get instant access to breaking news, the hottest reviews, great deals and helpful tips.
Kevin started taking PCs apart in the 90s when Quake was on the way and his PC lacked the required components. Since then, he’s loved all things PC-related and cool gadgets ranging from the New Nintendo 3DS to Android tablets. He is currently a contributor at Digital Trends, writing about everything from computers to how-to content on Windows and Macs to reviews of the latest laptops from HP, Dell, Lenovo, and more.
-
worst3 can you recharge it? and would it release oxygen when you do. or dose it just get clogged with oxygen and become useless?Reply
seem like a good idea except of NASA -
jacobdrj Sounds like a perpetual motion machine trying to shatter the 2nd law of thermodynamics...Reply
Where is the energy coming from? -
coopchennick How would it work in a sealed phone like the iphone?Reply
Won't the battery need more or less constant contact with the air? I don't want a battery sticking out the back of my phone... -
Humans think worst3seem like a good idea except of NASAThat's funny!Reply
jacobdrjSounds like a perpetual motion machine trying to shatter the 2nd law of thermodynamics...Where is the energy coming from?I didn't also understand how it really works I guess it is like "2*H2+02->2H20(ash)+thermal energy" then you apply electrical current and it becomes "electrical energy + 2H20 -> 2*H2(fuel) + 02". I guess they found a way to do "carbon fuel + 02 -> carbon ash + electrical energy" when you plug it in again "carbon ash + electrical energy -> carbon fuel + 02"
worst3and would it release oxygen when you do.I guess if my guess is correct it should.
It is a genius idea if this is how it works. And from its ashes fuel would be reborn. Of course, i speculate it will have thermal losses and of course some tearing of the material
-
astrotrain1000 They are calling this a battery not an energy source so I don't think perpetual motion is what they have in mind. It seems like to me that something in this battery reacts with the air to produces electricity, probably reaching a cap or saturation point. Then you'd have to go home and plug you battery into something to "drain" your battery of the oxygen. All standard loses to heat would apply just that the actuall storage of energy would be higher than lithium.Reply -
anamaniac An intriguing idea.Reply
Someone give these guys more funding to see what they can do. :)
Also, though it stores more energy, how efficient would it be?
How much does the charge dwindle over time? Simply cut the airflow to preserve battery life?
How many times could it be recharged?
In theory, this would be an excellent step for electric cars, because chemical battery storage is expensive, consumes a lot of volume, and inefficient, and recycling is needed.
Instead if getting 100 miles on a charge, getting 1000 miles or more would be awesome. Being cheaper in the first place you could use more batteries.
It'll be wonderful to see were this goes for now, and I do hope it lives up to its potential. I can wait 5 years. -
grieve I dunno... something seems fishy here.Reply
This is almost perpetual motion, except the carbon component would have to be changed im sure.
"" Oxygen is freely drawn in from the air and reacts within the pores of the carbon component, creating a constant "flow" of energy, or as Bruce states, a reagent, continuously recharging the battery as it discharges.""
SOOO if it is constantly recharging it would not have to be very large?
This battery will take over the earth's power needs... Just get a battery large enough to power a factory or your home/car/everything.
 Club Benefits
Club Benefits










